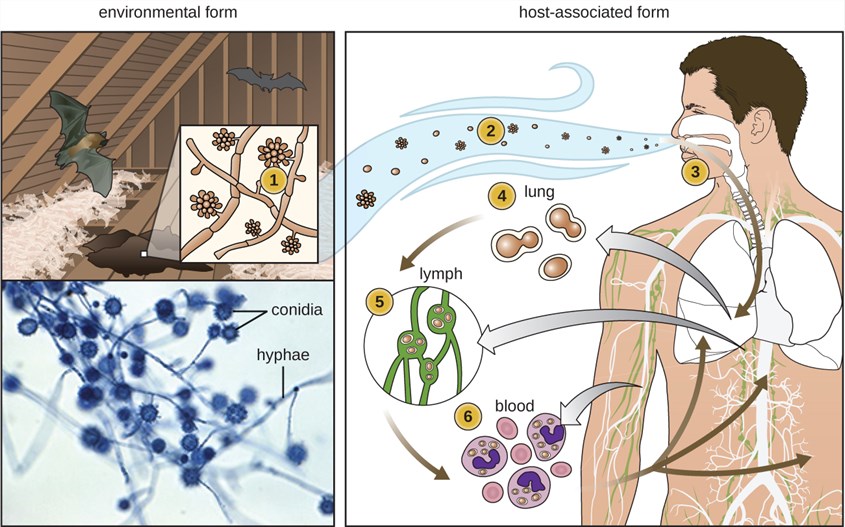
How does Fungal Infection affect the Environment?
Fungal infection can have a significant impact on the environment. It negatively affect the health of ecosystems, as certain species may be more vulnerable to fungal diseases, leading to population declines or local extinctions. Some fungal infections can affect plant growth and population, reducing the number of trees and plants in an area and disrupting the balance of the ecosystem. It can also cause damage to the soil, leading to soil erosion and a decrease in soil fertility. Moreover, it can also cause disease in animals, reducing their populations and impacting the food chain. Also, Fungi are important decomposers in the environment, breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients. Hence, it can also affect air quality, as some species produce toxins or allergens that can be dispersed into the air.
Finally, fungal infection can lead to the contamination of water sources, which can damage aquatic ecosystems. Fungi can cause a variety of diseases in humans, animals, and plants. In humans, they can cause skin, nail, and respiratory infections. In animals, they can cause skin, respiratory, and digestive problems. In plants, they can cause blight and rot.
Causes of Fungal Infection
Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which are microscopic organisms that live on the dead tissues of plants and animals, as well as on living organisms such as humans. The most common types of fungal infections include athlete’s foot, jock itch, ringworm, and yeast infections. These infections are generally caused by contact with contaminated surfaces, such as floors and shower stalls, or by direct contact with an infected person. Fungi can also spread through the air, through contact with infected animals, or through contaminated food or drink. In some cases, fungal infections can be caused by a weakened immune system.
How Fungal Infection Spreads
Fungal infections are caused by microorganisms such as yeast, molds and fungi. These fungi are found naturally in soil, air, water, plants, animals, and can spread to humans and other animals through contact or inhalation. The ways through which they can spread are direct contact with an infected person, with soil or water, insect bites, airborne spores, and can be difficult to control or eradicate. Fungal spores released into the air can spread throughout the atmosphere and can cause allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and other health issues. Fungal infections typically cause skin rashes, itching, and other uncomfortable symptoms. In severe cases, they can cause organ damage or even death. Few of the Fungal infection found in humans are Athlete's Foot (Tinea Pedis), Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris), Ringworm (Tinea Corporis), Nail Fungal Infection (Onychomycosis).
Types of Environmental Fungal Infection
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
- Aspergilloma
- Aspergillosis
- Blastomycosis
- Candidiasis (Yeast Infection)
- Cryptococcosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
- Mucormycosis
- Zygomycosis
Few of the Major Symptoms of Environmental Fungal Infection are
- Skin irritation: Fungal infections often cause skin irritation, such as itching, redness, and rashes.
- Respiratory symptoms: Inhaling fungal spores can cause coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
- Nail changes: Fungal infections can cause discoloration, thickening, and separation of the nail from the nail bed.
- Digestive symptoms: Fungal infections can cause abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and diarrhea.
- Systemic symptoms: In rare cases, a serious fungal infection can spread throughout the body and cause fever, chills, fatigue, and weight loss.
Treatment to Eliminate Environmental Fungal Infections
Treatment for environmental fungal infections typically depends on the type of infection, and the severity of symptoms. In general, antifungal medications are the most effective way to eliminate a fungal infection. Antifungal medications such as fluconazole, itraconazole, terbinafine, and amphotericin B may be prescribed to treat fungal skin infections. Inhaled antifungal medications may be prescribed for fungal lung infections. Oral antifungal medications may be prescribed for internal fungal infections. Common treatments include antifungal creams or ointments, oral antifungal medications, or a combination of both. In some cases, a topical or oral steroid may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove fungal growths or infected tissue. Additionally, it is important to practice good hygiene, keep the affected area clean and dry, and avoid sharing personal items with others to prevent the spread of infections.





